
Treatment of Periodontitis
When gum disease develops into periodontitis it cannot be cured, only controlled. Left untreated, periodontitis will increasingly damage the supporting structures of your teeth, including both the gum tissues and jaw bone. This means that once periodontitis reaches an advanced stage, without dental intervention, tooth or bone loss can occur.
Periodontitis is a major cause of tooth loss in adults and is a serious health issue that requires ongoing gum disease treatment. While gingivitis or the first stage of gum disease can be reversed, it often goes undetected. If you notice any sensitivity, swollen gums or bleeding gums it’s important to schedule a check-up with your dentist or periodontist.
Schedule your periodontal health appointment with Putney Dental Care by calling (02) 9808 2588 or contact us online. We use the latest techniques in the dental treatment of periodontitis to provide supportive periodontal care in Sydney to the suburbs of Putney, Ryde, Gladesville, Meadowbank, Tennyson Point and surrounding areas.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is an advanced gum disease that progressively affects the supporting structures of all teeth, including gum tissue and the jaw bone. It is caused by destructive bacteria in dental plaque forming under the gum line. Overtime periodontitis can lead to the gums separating from the teeth and forming periodontal pockets, gum recession, tooth sensitivity, exposed roots of teeth, loose teeth, tooth loss and even bone loss.
Commonly seen in adults, gum disease is largely preventable with consistent good oral hygiene practices that include brushing your teeth twice daily, flossing and visiting your dentist regularly.
Is Periodontitis a Serious Disease?
Periodontitis is a very serious and advanced periodontal disease that cannot be reversed, only managed and slowed down by ongoing dental treatments and preventative at-home dental care. Without treatment, periodontitis can end up destroying gum tissues and underlying jaw bones that hold your teeth in place. It can progressively change from sensitivity, bleeding gums and pain while chewing to bone loss and tooth loss, as well as other significant health issues.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
The main cause of periodontal disease is dental plaque. This sticky, painless and mostly clear film that coats your teeth contains harmful bacteria. When plaque isn’t cleaned away from your teeth and gums properly, it can harden into tartar, also called calculus, and build up around and underneath the gums, causing gum disease.
Risk factors for gum disease are:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Genetic factors or history of gum disease
- Poor nutrition and stress
- Smoking, chewing tobacco or illicit drug use
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Crooked teeth or hard to clean teeth
- Teeth bridges that don’t fit properly
- Defective teeth fillings
- Medications that cause dry mouth
- Diabetes and illnesses that affect the immune system such as cancer and HIV/AIDS
- Female hormonal changes such as puberty, pregnancy or menopause
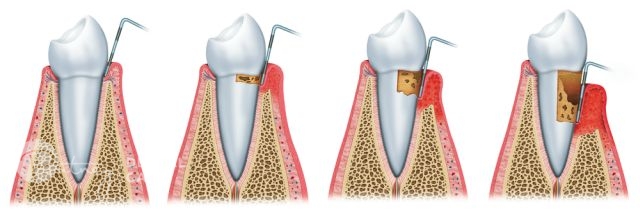
Stages of Gum Disease
Gum or periodontal disease starts out as gingivitis. When left untreated, gingivitis will turn into periodontitis. While gingivitis can be reversed, periodontitis is a lifelong condition that can only be managed and slowed down with dental treatments.
The stages of gum disease are:
- Stage 1 – Gingivitis: plaque irritates gums, causing them to be red, inflamed and bleed.
- Stage 2 – Periodontitis: gums recede backwards and separate from the tooth allowing tartar and bacteria to build up above and below gums, causing damage to the bone and tooth structures.
- Stage 3 – Severe or Advanced Periodontitis: further gum recession and pronounced separation of gums from teeth called periodontal pockets, the bone structure breaks down, teeth loosen, pus accumulates, soreness while chewing and there is potential for tooth loss or multiple teeth loss.
Individual treatment options for gum disease are based on what stage has been reached and how quickly the disease is progressing, from slow to rapid. Younger people are susceptible to a more rapid progression of gum disease and should seek dental treatments urgently.
Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatments
The aim of any gum disease treatment is to control bacterial infection. Once periodontitis or stage 2 of gum disease occurs, it is irreversible. However, with early intervention and good oral care, periodontitis can be slowed down and managed with non-surgical periodontal treatments that help preserve your teeth and gums.
Periodontal Cleaning
Periodontal cleaning, also called debridement, is a non-surgical periodontal treatment for gum disease that has been caught early and hasn’t damaged any structures below the gum line. Effective as an ongoing tooth surface treatment in early stage periodontal disease.
Built up plaque and tartar will be removed between and around the teeth using manual tools or dental technology such as ultrasonic vibrations with water and air polishing. Topical numbing medication and local anaesthesia may be applied to keep the treatment as painless as possible. Afterwards, you may feel slight pain and sensitivity.
If periodontal infections aren’t removed successfully then you may require further treatment. This is the case when periodontitis spreads below the gum line or when gingival pockets develop between teeth and gums.
Root Planing and Scaling
Scaling and root planing clean deep within the pockets between gums and tooth surfaces. Using manual or ultrasonic tools, scaling starts the process by removing built up plaque and tartar that is deep below the gum line and between teeth. Then root planing smoothes out the tooth from the root surfaces to help the gum reattach and reduce gingival pocket depth.
As an effective non-surgical treatment for gum disease, scaling and root planing usually takes place over two or more appointments to allow time for gums to heal. During treatments, patients will have their gums numbed using our virtually painless local anaesthetic technology.
Slight sensitivity and pain may be felt afterwards for up to 1 week. While root planing and scaling may stimulate the regeneration of gum tissue, it also carries the risk of gum recession and in rare cases, the potential for nerve damage. There is also no guarantee that your gums will reattach to your teeth.
Medications
Antibiotic medications are often given after non-surgical periodontal deep cleaning treatments to mitigate any risks of further infection of the gums. During scaling and root planing treatment, the periodontal pocket separating gums from teeth is also flushed with antiseptic medication to soothe inflammation or stop the infection from spreading deeper into the bone.
Antibiotics may be prescribed in the form of tablets, mouthwash, toothpaste or topically to the gums. They will reduce or temporarily kill bacterial plaque progressing periodontal disease. If the infection persists, further medications or dental treatments may be needed.
Surgical Periodontal Treatments
Surgical treatments are usually required for patients with stage 3 or severe periodontitis. Or in cases where non-surgical periodontal treatments have been unsuccessful in managing aggressive periodontitis. They can effectively stabilise gum health and stop increased damage to teeth, gums and below the bone structure where possible.
Tooth Extraction and Dental Implants
Where periodontitis is extremely severe, extensive dental surgery may be the most beneficial solution for oral health long term. Especially when teeth have become loose, cracked or fallen out. This will involve removing the infected tooth and treating the surrounding gums.
Dental implants provide a solution to areas where teeth are missing, restoring your smile and overall oral function. Designed to look and operate like natural teeth, dental implants are an expensive and lengthy process that involves fusing a metal bolt into the jaw bone and adding a dental crown. Complications are low, however, receding gums may also appear over time.
Pocket Depth Reduction
In pocket depth reduction surgery or flap surgery, the aim is for the spaces between the teeth and gums to return to their natural snug state and remove the infection. First, tiny incisions are made in the affected gum areas so that the tooth root can be exposed for scaling and root planing. Then the underlying bone is reshaped if it was damaged, before the gum tissue is tightened and stitched back into place.
Pocket reduction surgery is usually an in-clinic day procedure. Post treatment you will experience mild to moderate pain and swelling for a few days. Adversely, your treated tooth might develop greater sensitivity to hot and cold, and you’ll be more susceptible to increased gum recession over time.
Root Coverage with Gum Tissue
When periodontitis has progressed to a stage where your tooth’s roots are exposed due to gum recession, you may require root coverage or soft tissue grafts. Essentially this procedure reinforces your gum with soft tissue, commonly taken from the palate or roof of your mouth, and attaches it to the affected area with stitches.
Aimed to achieve the most aesthetically pleasing outcome, this procedure improves gum health and helps reduce further gum recession, root exposure and tooth sensitivity. Root coverage can be performed at your dentist’s under local anaesthesia.
Root planing and scaling are also performed prior to this procedure and surgical material will be placed over the tissue graft to protect it. Healing can take up to 8 weeks and post operative care must be followed to reduce complications.
Regenerative Surgery
Regenerative surgery such as dental bone grafting helps to restore and encourage the bone growth surrounding teeth that have been destroyed by periodontitis. Dental bone grafts are made from small fragments of your own bone, from a donor or created synthetically.
Regenerative bone grafting typically is a safe and effective in-clinic or outpatient dental procedure, under general anaesthesia. After incisions are made pull the gum back, scaling and root planing are performed before the bone graft is fused to the affected area and the gum is reinstated with stitches. The expected risks are the same as any extensive dental surgery and healing can take up to 9 months.
In conjunction with other surgical periodontal treatments, membranes or guided tissue regeneration can also be applied in between teeth and gums to help create a stronger fusion between them. Additionally, regenerative tissue stimulating proteins can be applied topically in a gel to diseased roots of teeth to encourage healing and growth of healthy bone and tissue.
Ongoing Care with Periodontal Disease
Periodontitis is a lifelong condition that needs ongoing care in partnership with your dentist or periodontist. This includes good dental care at home daily, regular check ups and treatments.
Non-surgical periodontal treatments are usually advised to be repeated every 3-4 months to maintain gum health. Whereas, for chronic periodontitis, your dentist will discuss ongoing care in line with your tailored surgical periodontal procedure.
How to Prevent Periodontal Disease
Regular and consistent preventative care for good oral hygiene is the best way to combat periodontal disease. Not only will it be helpful in reducing your chances of developing gum disease, but it will also increase the success of periodontitis treatments.
Prevent gum disease by:
- Brushing teeth twice daily and flossing daily to ensure healthy gums
- Regular dental check-ups every 6 months or more depending on your risk factors
- Quit tobacco and consumption of things harmful to your teeth
- Maintain a balanced diet
If you notice symptoms of gum disease, it’s important that you seek advice from your dentist as soon as possible to treat gum disease and avoid any irreversible damage.
Expert Periodontic Services with Putney Dental Care
Our expert, highly skilled periodontal gum specialists will conduct a full examination of your mouth, conduct dental x-rays and 3D imaging to diagnose periodontitis and establish the severity of your gum disease. They will then design a holistic treatment plan tailored to you that includes removing infection and restoring the function and aesthetics of your smile.
For more information about periodontal diseases, or to schedule an appointment, contact Putney Dental Care today.
We service areas in Sydney including Putney, Ryde, Meadowbank, Gladesville, Tennyson Point and surrounding suburbs.
Periodontal Services in Putney
Address
A. Suite 5, 227 Morrison Rd, Putney, NSW 2112
(Next Door To Royal Rehab)
Reserved Parking Available At Rear.
Opening Hours
Monday – 8:30 am – 5:30 pm
Tuesday – 8:30 am – 5:30 pm
Wednesday – 8:30 am – 5:30 pm
Thursday – 8:30 am – 5:30 pm
Friday – 8:30 am – 5:30 pm
Saturday – 8:00 am – 1:00 pm
Emergency Appointments Available
Call us today on (02) 9808 2588 or book an appointment online.
Book Online